

Other typical operations supported by the hardware are circular buffers and lookup tables.
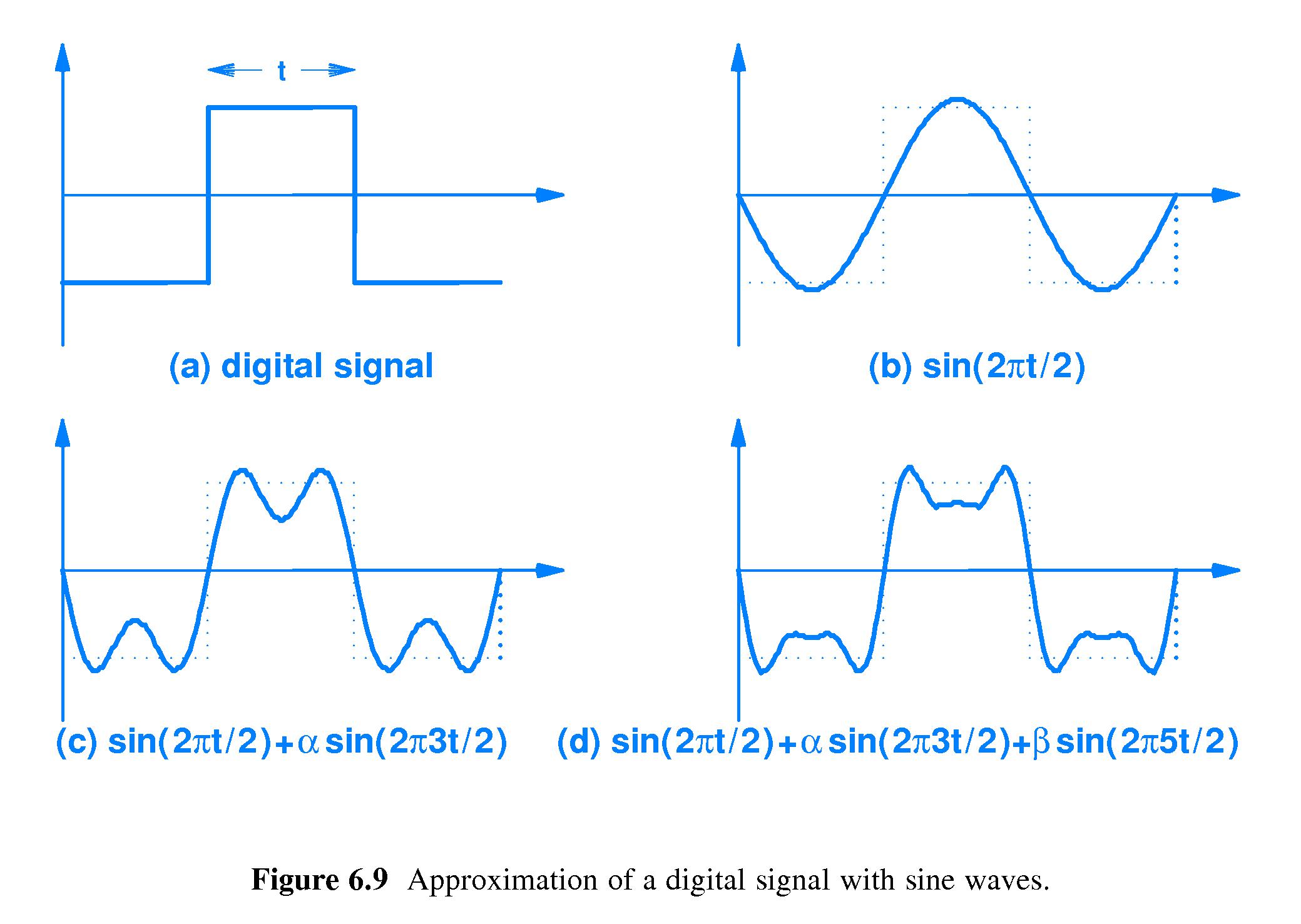
Typical arithmetical operations include fixed-point and floating-point, real-valued and complex-valued, multiplication and addition. Processing is done by general-purpose computers or by digital circuits such as ASICs, field-programmable gate arrays or specialized digital signal processors (DSP chips). The concept of discrete-time signal processing also refers to a theoretical discipline that establishes a mathematical basis for digital signal processing, without taking quantization error into consideration.ĭigital signal processing is the processing of digitized discrete-time sampled signals. This technology was a predecessor of digital signal processing (see below), and is still used in advanced processing of gigahertz signals. This technology mainly discusses the modeling of a linear time-invariant continuous system, integral of the system's zero-state response, setting up system function and the continuous time filtering of deterministic signalsĭiscrete-time signal processing is for sampled signals, defined only at discrete points in time, and as such are quantized in time, but not in magnitude.Īnalog discrete-time signal processing is a technology based on electronic devices such as sample and hold circuits, analog time-division multiplexers, analog delay lines and analog feedback shift registers. The methods of signal processing include time domain, frequency domain, and complex frequency domain.

Nonlinear circuits include compandors, multipliers ( frequency mixers, voltage-controlled amplifiers), voltage-controlled filters, voltage-controlled oscillators, and phase-locked loops.Ĭontinuous-time signal processing is for signals that vary with the change of continuous domain (without considering some individual interrupted points).
The former are, for instance, passive filters, active filters, additive mixers, integrators, and delay lines. This involves linear electronic circuits as well as nonlinear ones. Categories Analog Īnalog signal processing is for signals that have not been digitized, as in most 20th-century radio, telephone, and television systems. Signal processing matured and flourished in the 1960s and 1970s, and digital signal processing became widely used with specialized digital signal processor chips in the 1980s. The paper laid the groundwork for later development of information communication systems and the processing of signals for transmission. In 1948, Claude Shannon wrote the influential paper " A Mathematical Theory of Communication" which was published in the Bell System Technical Journal. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control systems of the 1940s and 1950s. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis techniques of the 17th century. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal. Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing signals, such as sound, images, potential fields, seismic signals, altimetry processing, and scientific measurements. The signal on the left looks like noise, but the signal processing technique known as spectral density estimation shows (right) that it contains five well-defined frequency components.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
